News
Research on high-temperature lithium-manganese battery cathode materials
2024-01-12
Author:
High-temperature lithium manganese dioxide battery is an important primary power source, which is widely used in automobile tire pressure detection system (TPMS) as well as medical instruments and other fields. Although China is a big manufacturer of primary batteries, the field of high-temperature lithium primary batteries is in a blank state. The lack of anode materials suitable for high temperature applications is one of the reasons limiting the development of high temperature lithium manganese dioxide batteries. The reaction between manganese dioxide and electrolyte above 100 ℃ becomes gradually strong, prompting the electrolyte to decompose and produce a large number of gases, and the formation of an inert oxide layer on the surface of manganese dioxide causes an increase in ohmic polarization, and so on and so forth, resulting in the deterioration of the performance of lithium manganese dioxide batteries at high temperatures, which can't work.
Our company has carried out in-depth research on manganese dioxide anode materials suitable for high temperature, starting from the control of the ratio of manganese dioxide γ and β crystal type, and elemental doping to obtain high-temperature type manganese dioxide (G-MnO2).
Material performance test methods:
Positive electrode wafers were made by laminating the film in the ratio of high-temperature manganese dioxide: conductive agent: adhesive = 92:4:4, with ethanol as solvent.
The resulting cathode sheet was assembled with lithium wafers, polypropylene diaphragm and electrolyte to become a CR2032 battery for testing.
Battery test results:
1. Discharged at room temperature (20±5 °C) with stage constant current (8-3-1.5-0.6-0.3 mA/g) and cutoff voltage of 2.0 V, the specific capacity of anode material was 264 mAh/g.
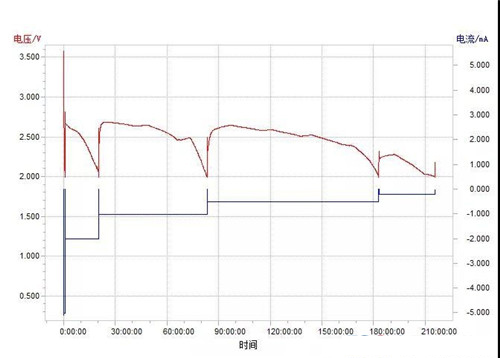
2. The material was discharged at low temperature (0±2 °C) at a stage constant current (16-8-3-1.5-0.6-0.3 mA/g) and the discharge curve was subjected to fluctuations due to temperature variations, and the discharge specific capacity of the material was 261 mAh/g.
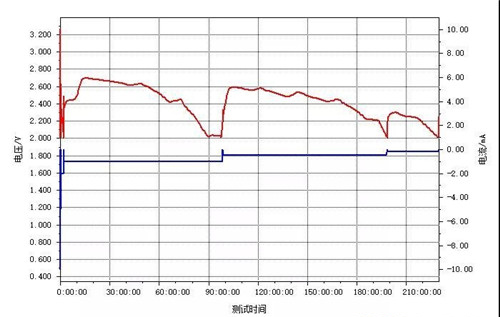
3. Under the high temperature of 125 ℃, the battery was discharged at constant current of 16 mA/g with a cut-off voltage of 2.0 V. The battery could be discharged normally and the discharge curve was smooth, and the specific capacity of the cathode material was 260 mAh/g. Obviously, the material has a better capability of high-current discharging under high temperature.
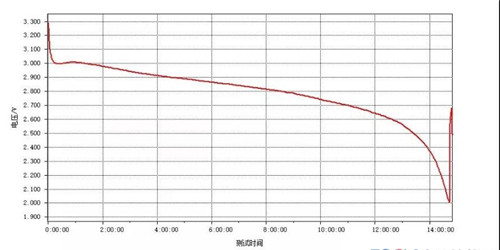
4. The battery was set aside at 125 ℃ for 120 hours, and then discharged at a constant current of 16 mA/g with a discharge cutoff voltage of 2.0 V. The specific capacity of the cathode material was 250 mAh/g, indicating that the high-temperature type cathode material remained relatively stable at 125 ℃, and that the degree of decomposition or degradation occurred was small.
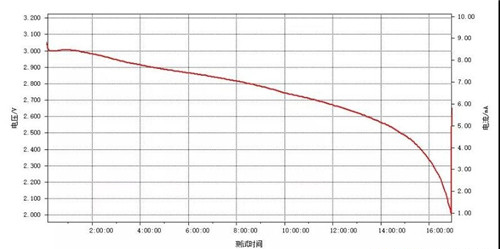
5. The battery was discharged at 150 ℃ with a constant current of 16 mA/g and tested for 8 hours, exceeding the requirement of the TPMS system to work at 150 ℃ for 7 hours. The working voltage platform of the battery is normal, no abnormal platform, indicating that there is no new phase generated in the cathode material, the nature is stable, and the battery can continue to be discharged.
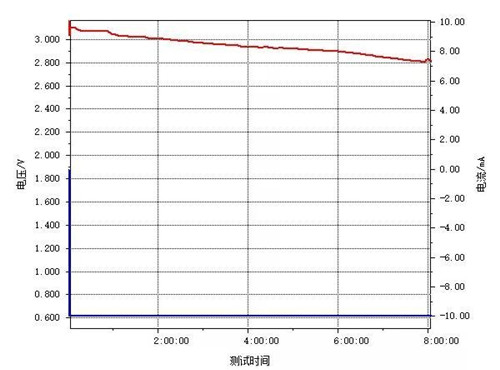
The CR2032 battery made of the high temperature manganese dioxide material developed by our company was tested for electrical performance and shelf life durability at room temperature, low temperature and high temperature (125 ℃, 150 ℃). The specific capacity of this material reaches more than 260 mAh/g, and the discharge curve is smooth, while the manganese dioxide material remains relatively stable at high temperature. This material is fully suitable for working under high temperature and can be used as the cathode material of TPMS batteries.
RELATED INFORMATION
undefined





